Spatial Computing Applications Across Industries
Spatial computing has the potential to transform various industries, driving innovation, efficiency, and new ways of working.
Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
A few ways spatial computing can be used in logistics:
Route planning for warehouse management, assisting staff with moving product quickly and easily
Virtualized control center for warehouse supervisors, allowing them to manage the entire supply chain
Guided step by step instructions for assembly line workers with improved compliance and safety measures in operations
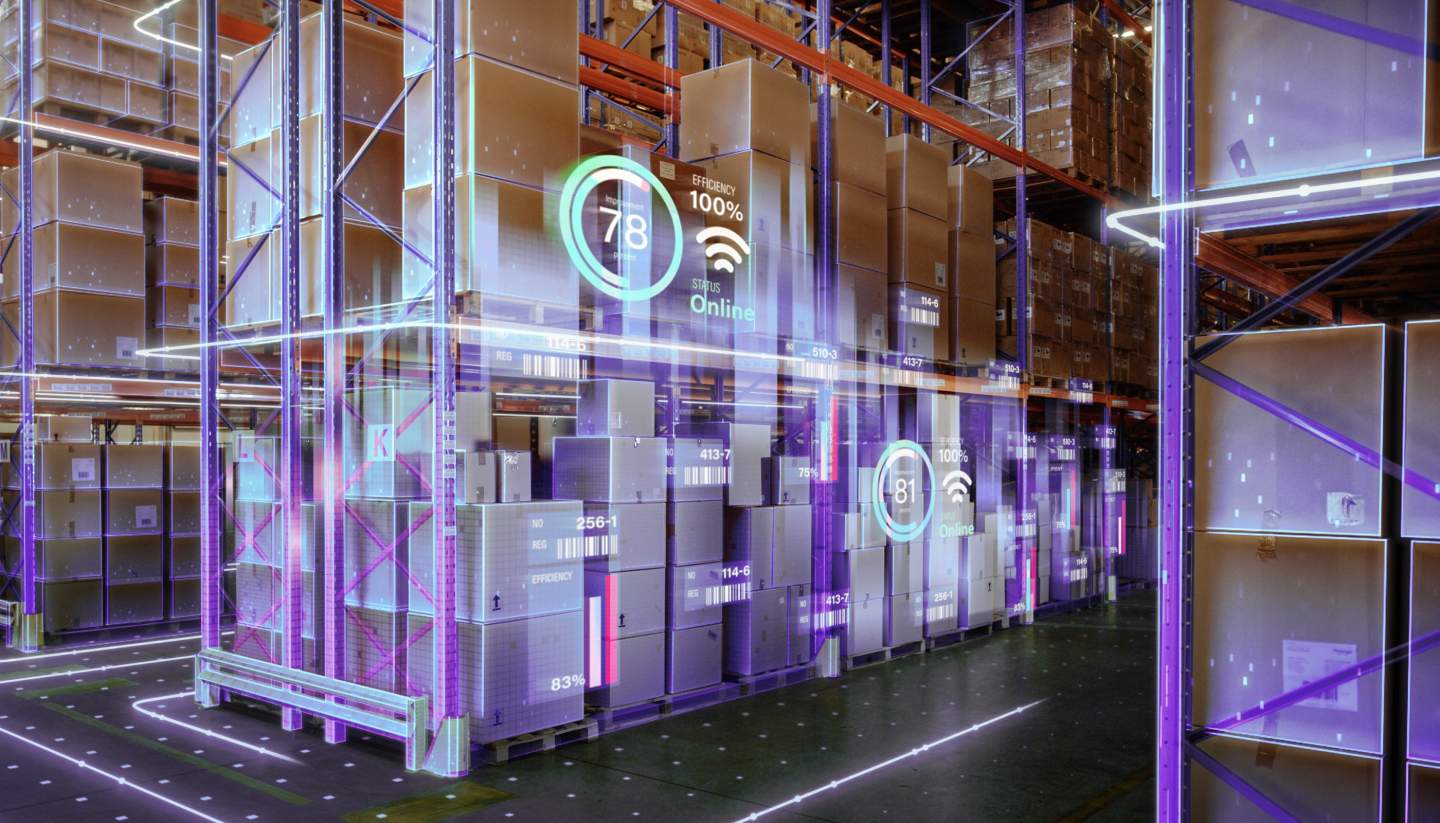
Companies can use spatial computing technologies to improve the flow of goods and materials in their supply chains. By integrating location data, sensors, and real-time analytics, they can track shipments, optimize routes, and efficiently manage inventory. For managers, the Vision Pro can optimize warehouse operations and streamline inventory management. This kind of technology can provide a holistic view of the entire supply chain, allowing managers to identify bottlenecks, optimize routes, and simulate various scenarios to improve efficiency and resilience.
Workers too can benefit from this kind of technology, receiving real-time information about product locations, stock levels, and picking routes through AR overlays, increasing efficiency and reducing errors. The Vision Pro can guide workers through the warehouse, highlighting the most efficient routes and providing visual cues for item selection and placement. Workers can also get required product information and assembly instructions as they go about their work in a hands free environment.
Location-based Marketing and Retail
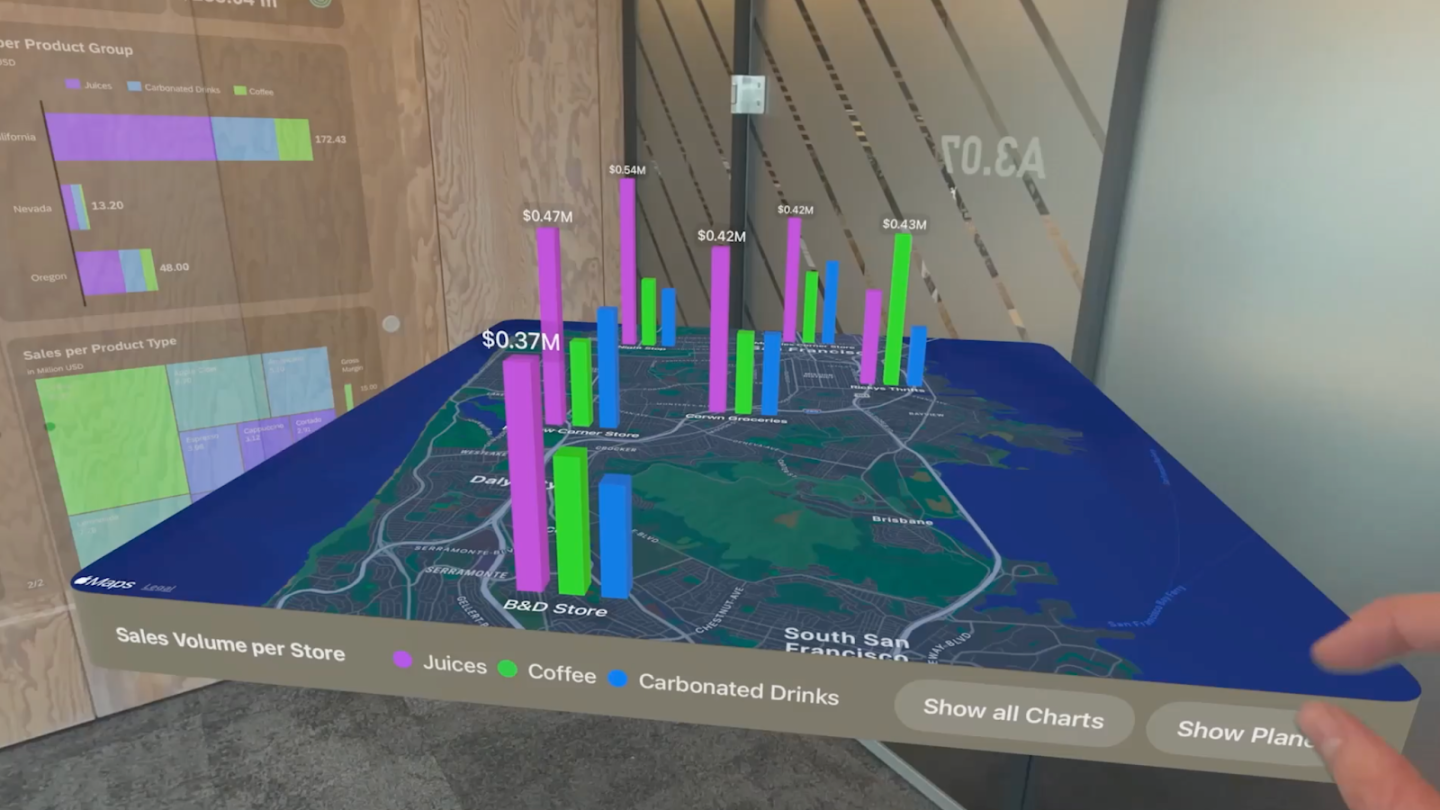
Retailers and marketing companies use spatial computing to create location-based advertising and personalized offers. By analyzing customer movements and behaviors in physical stores, they can target promotions to specific demographics.
Retailers can adopt spatial computing for applications like:
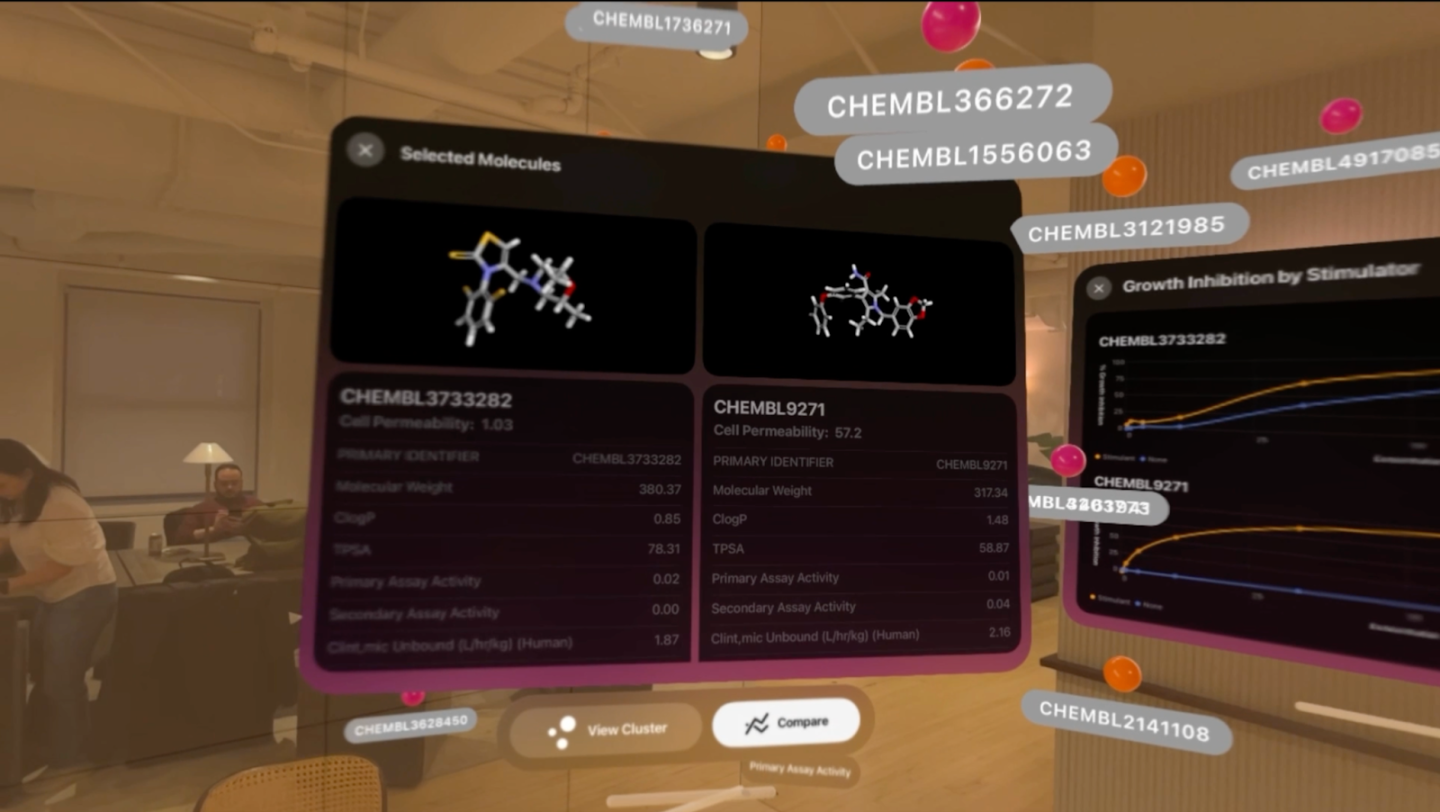
Spatial computing can revolutionize the retail industry by enhancing customer experiences and streamlining store operations. Retailers can use AR and VR applications to provide personalized product recommendations, help customers visualize products in their homes, or even simulate entire shopping experiences. For high end products that come with a lot of configuration options, the Vision Pro allows a user to modify and configure products to their exact specifications - seeing the change in real time. This level of immersive interaction not only attracts and retains customers but also encourages more purchases, ultimately benefiting the retail sector.
For example, shoppers can visualize furniture in their own home through mobile AR before purchasing. Or virtually "try on" clothing by seeing it overlaid on live images of themselves. Spatial computing promises to blend the advantages of in-store experiences with online convenience.
In product configuration and space design, the Vision Pro can enable customers and designers to visualize and customize products or spaces in real-time, making the design process more interactive and engaging. This can lead to better customer satisfaction, reduced design iterations, and faster time-to-market.
Smart Buildings, Facility Management, and Space Design
Spatial computing is used to create smart buildings that automatically optimize resources such as lighting, heating, and air conditioning. Integrating sensors and data analytics allows companies to improve energy efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance the work environment for employees.
How the Vision Pro could be used:
Virtual tours of home remodels, allowing customers to experience a designer’s plans rather than simply looking at 2d renderings
AR assistance during facility maintenance visits, allowing for relevant manuals and other information to be displayed while making repairs
Create new building and space designs that can be seen and experienced virtually, without the cost of construction
The integration of spatial computing in interior design offers new possibilities for visualizing and planning spaces. Technologies like augmented reality enable users to project virtual representations of furniture and decor into their actual environments, facilitating a more informed and creative design process. This approach allows for a realistic preview of design choices in real contexts, enhancing the ability to assess aesthetics, function, and spatial compatibility without the need for physical prototypes. A notable example of this in practice is IKEA's application, IKEA Place, which allows users to visualize how IKEA's furniture would fit and look in their own spaces, illustrating the practical application of spatial computing in enhancing interior design.
Cities and municipalities use spatial computing to plan and optimize urban spaces. Analyzing traffic flows, demographic data, and urban infrastructures, they can make informed decisions to improve quality of life, address traffic issues, and promote sustainable development. And the architects and designers get to experience what a newly imagined space would look like, without the upfront construction costs.
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, spatial computing is used to implement augmented reality (AR) in production processes. Employees can use AR glasses to receive digital instructions and visual aids in real-time, leading to improved efficiency, error reduction, and training opportunities.
Spatial computing could be useful in manufacturing:
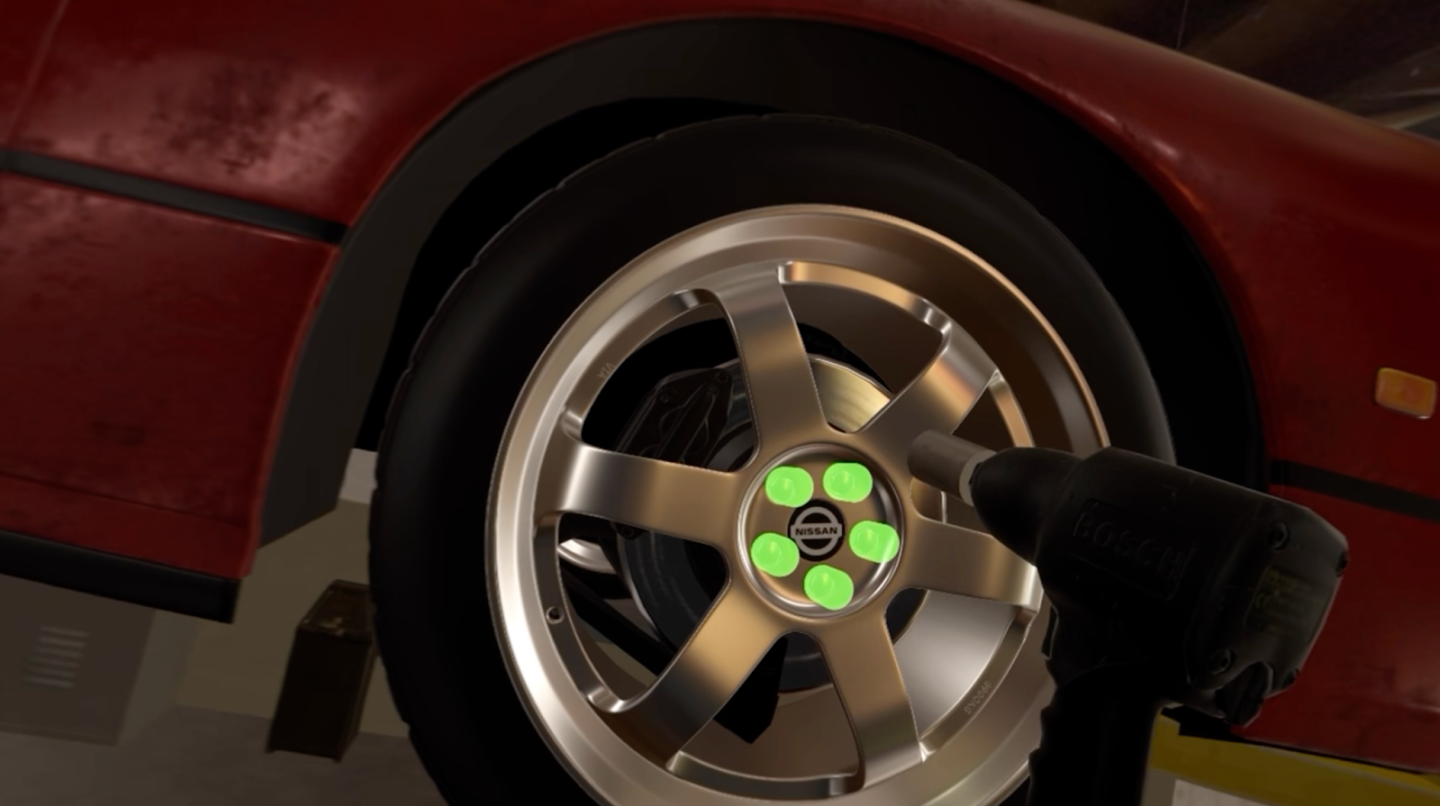
Virtual training of working with equipment on manufacturing lines that might otherwise be hazardous for untrained workers to use for learning
Guided assistance while doing maintenance or other processes such as change over on a manufacturing line from one product to another
Virtualized control room for supervisors, allowing them to leverage the infinite canvas to see deeper into how the lines are runnings
In the manufacturing domain, spatial computing allows factories to optimize processes and better understand their machines' performance. By seamlessly integrating digital and physical spaces, operators can monitor equipment in real-time and detect potential issues before they become critical. This technology enables more efficient management of factory resources and ultimately improves manufacturing outcomes.
Manufacturing was one of the first industries to embrace spatial computing. Several already use spatial devices to remotely assist workers, display virtual work instructions, and capture soft knowledge before operators retire. From assembling parts on the line to quality assurance and assisting operators, spatial computing has measured success.
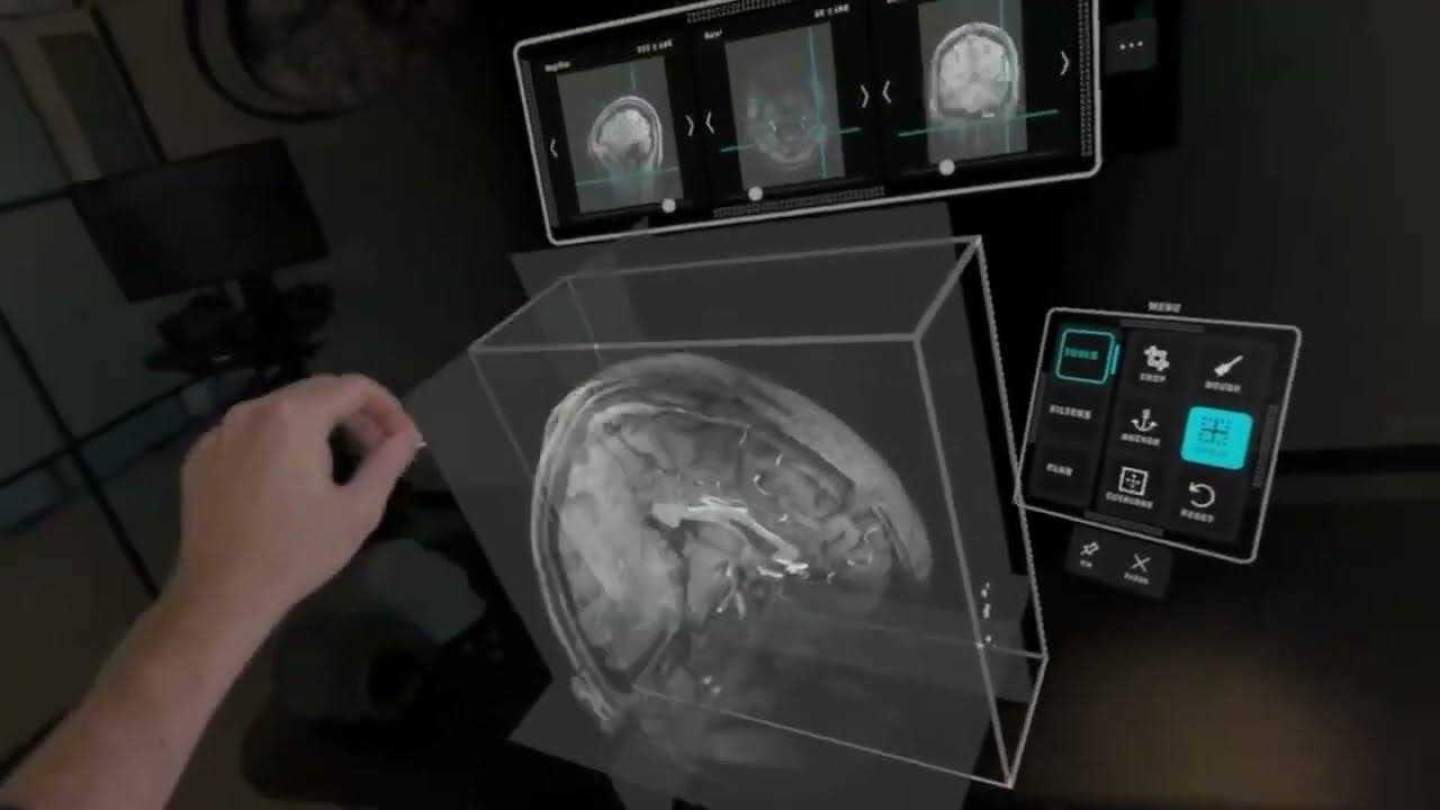
Spatial computing is a natural fit for fields like engineering and architecture that rely on 3D modeling and visualization. By integrating digital models directly into real-world physical contexts, spatial computing enables more rapid iteration, collaborative design and interactive simulation. Engineers can visualize and manipulate virtual prototypes and digital twins overlaid right on the factory floor or building site using AR headsets.