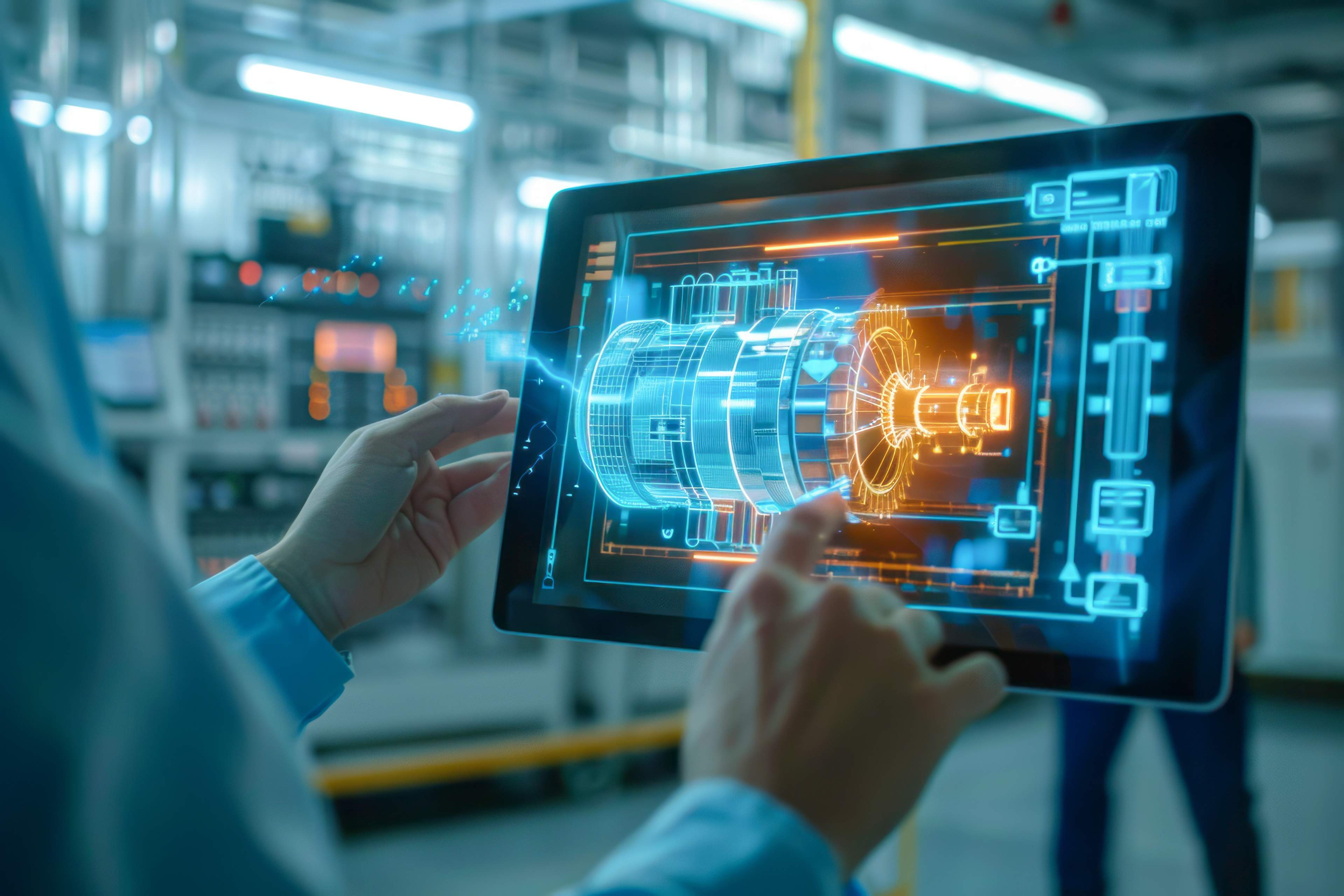
How manufacturing executives can build a comprehensive digital twin strategy that drives operational excellence, enables predictive decision-making, and accelerates Industry 4.0 transformation
Key takeaways:
- Manufacturing leaders must align digital twin initiatives with broader digital transformation strategies to ensure organizational readiness and maximize value creation.
- Successful digital twin implementation requires a comprehensive data strategy that addresses governance, quality, and integration across multiple systems and stakeholders.
- Organizations need to develop new competencies and roles to effectively leverage digital twin insights, including data scientists, simulation experts, and cross-functional integration teams.
Manufacturing is on the cusp of a revolution. As the technologies of Industry 4.0 mature, the way we make decisions about operations, maintenance, and optimization is fundamentally changing. At the heart of this evolution is digital twin technology: a powerful tool promising to bridge the gap between physical assets and digital intelligence. Yet, for the actualization of a successful digital twin implementation, far more is needed than technological ability. It requires a comprehensive strategy considering an organization's readiness, data capabilities, and workforce development.
Building a strong foundation
Success in any digital twin initiative starts long before the first sensor is installed or the first simulation is run. Manufacturing leaders must assess an organization's digital maturity and readiness for this transformative technology to take shape by understanding your company's current capabilities, identifying gaps, and creating a roadmap for development aligned with broader business objectives.
This itself needs to be founded on a robust data strategy. When shortcuts are made, it risks several critical issues that can derail the implementation and lead to inadequate results. Here are some potential consequences:
1. Poor data quality
Without a clear governance framework, the data feeding into the digital twin may be incomplete, inconsistent, or inaccurate. This can lead to unreliable simulations and insights, undermining the value of the digital twin and eroding trust among stakeholders.
2. Data silos and integration
Manufacturing environments often consist of a mix of legacy systems and modern equipment. Without a robust strategy for integrating data across these systems, digital twins may fail to provide a holistic view of operations, limiting their ability to deliver actionable insights.
3. Inefficient decision-making
Digital twins are only as effective as the data they analyze. Without reliable, real-time data, the insights generated may not be timely or relevant, leading to delays or incorrect decisions that can impact operational performance and competitiveness.
4. Increased costs and wasted resources
Without a structured approach to data management, companies may need to invest additional time and resources to clean, standardize, and integrate data after the fact. This reactive approach can significantly increase the cost of implementation and delay the realization of benefits.
5. Limited scalability
A poorly thought-out data strategy can hinder the scalability of digital twin solutions. If initial implementations are not designed with broader organizational needs in mind, expanding their use may require significant rework and additional investments.
6. Misalignment with business goals
A lack of alignment between the digital twin’s data strategy and the company’s broader objectives can result in solutions that fail to deliver meaningful business outcomes. For example, insights might not align with key performance indicators (KPIs), making it difficult to measure success or justify further investment.
We recommend that organizations start with clearly outlined governance frameworks to ensure data quality, security, and accessibility. This ranges from developing protocols that manage data collection, validation, and integration across systems to the unique challenge of the manufacturing environment, which usually features both old and new systems operating together. Leaders must carefully think through how to bridge such technological gaps without losing efficiency in operations while also considering the humans involved in the work.
Just as it's important to think about the technical workflows of a digital twin, it's also critical that they enhance individual roles and responsibilities. Employees who have traditionally relied on manual processes or legacy systems may feel apprehensive about the shift to digital twin-enabled operations. One way to help is to invest in a comprehensive training program to ensure the workforce understands the purpose and potential of the digital twin and feels empowered to use it effectively, especially for those not accustomed to using technology in their day-to-day work.
Keep the lines of communication open, and inspire your team by discussing how these changes will improve day-to-day work and contribute to overall business success, which can help alleviate concerns and foster adoption.
Collaboration between teams is another critical factor. Bridging technological gaps often involves cross-functional efforts that require breaking down silos and promoting knowledge sharing. For example, IT and operations teams must work closely to ensure that data from physical systems is accurately captured and integrated into digital platforms. Similarly, input from front-line workers who operate the equipment daily can provide invaluable insights that improve the accuracy and utility of the digital twin.
Leaders must recognize that technology adoption is as much about culture as it is about systems. Building a culture of continuous learning and adaptability ensures that employees remain at the center of what you build, not in the background. By prioritizing the human element alongside the technical, organizations can create an environment where digital twins are not just implemented but embraced, driving sustainable improvements across the business.
The interconnected nature of excellence
Equally important is stakeholder alignment. The digital twin affects many functions, ranging from operations and maintenance to quality control and reaches to strategic planning. Each group has its own set of needs and views. Creating value propositions for each stakeholder group while putting in place effective communication channels will help maintain engagement throughout the transformation journey. This can be done by conducting interviews to understand their unique perspectives, needs, and more.
Stakeholder interviews should explore pain points, aspirations, and success metrics specific to each group, ensuring that the digital twin addresses their priorities. As the project evolves, foster regular feedback loops where stakeholders can voice concerns and see how their input shapes outcomes can build trust and ensure alignment.
Workshops and cross-functional meetings can also play a key role in surfacing synergies between departments and enabling shared ownership of the transformation. By prioritizing stakeholder insights, organizations can create tailored strategies that resonate across all levels of the business.
Workshops, particularly those focused on innovation, can effectively bring stakeholders together and align them around a shared vision for digital twin implementation. These workshops typically introduce participants to new methodologies—such as design thinking—while providing a structured environment to brainstorm, collaborate, and identify solutions to pressing challenges. Beyond the theoretical, the workshops also provide practical sessions where attendees can apply these principles directly to their work, fostering hands-on learning and real-world relevance.
However, it’s essential to recognize that workshops are just the beginning. As with innovation workshops, the true value lies in the follow-through. While the workshop can inspire stakeholders, generate ideas, and create initial alignment, it’s the ongoing commitment to applying those learnings and changing operational practices that drives sustained success. To ensure workshops translate into lasting impact, organizations should establish post-workshop initiatives such as cross-functional task forces, pilot projects, or regular follow-up sessions. These steps help institutionalize the ideas and collaborations sparked during the workshop, ensuring that they evolve into tangible outcomes.
Workshops should also be designed to surface technical opportunities and cultural and organizational barriers. For example, by engaging diverse participants from across the organization, workshops can reveal differing priorities, potential resistance points, and opportunities for greater synergy. Addressing these challenges early sets the stage for smoother implementation and broader acceptance of digital twin solutions. In this way, workshops act as a catalyst—a powerful starting point for aligning people, processes, and technology around a common goal.
As organizations move beyond the initial stages of stakeholder alignment and foundational planning, the focus naturally shifts toward the mechanisms that drive sustained excellence. Here lies the critical interplay of technical infrastructure, integrated processes, and the development of human capital—the pillars upon which successful digital twin initiatives are built. Understanding how these elements connect and reinforce one another is the key to unlocking the full potential of digital twins.